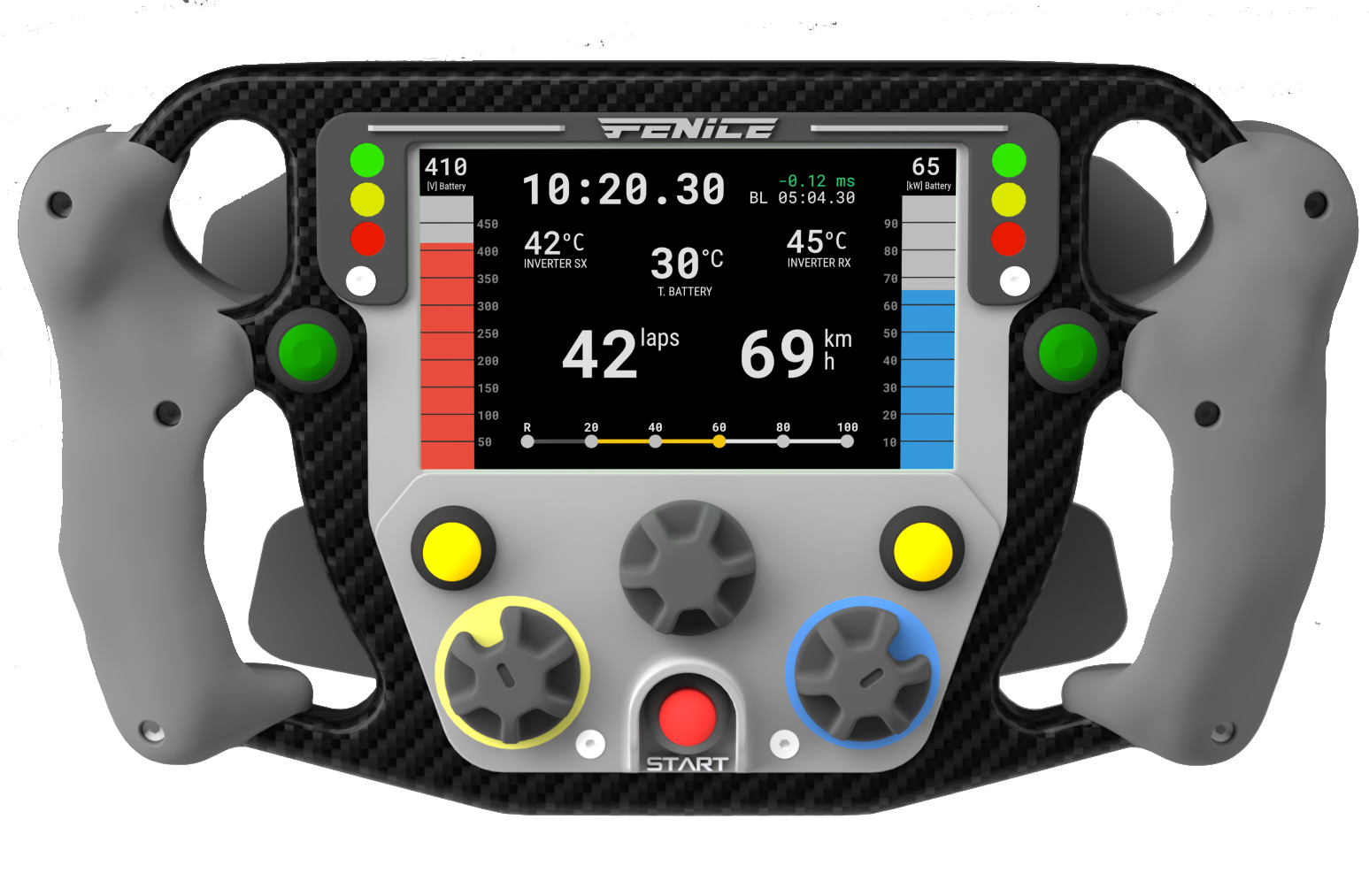
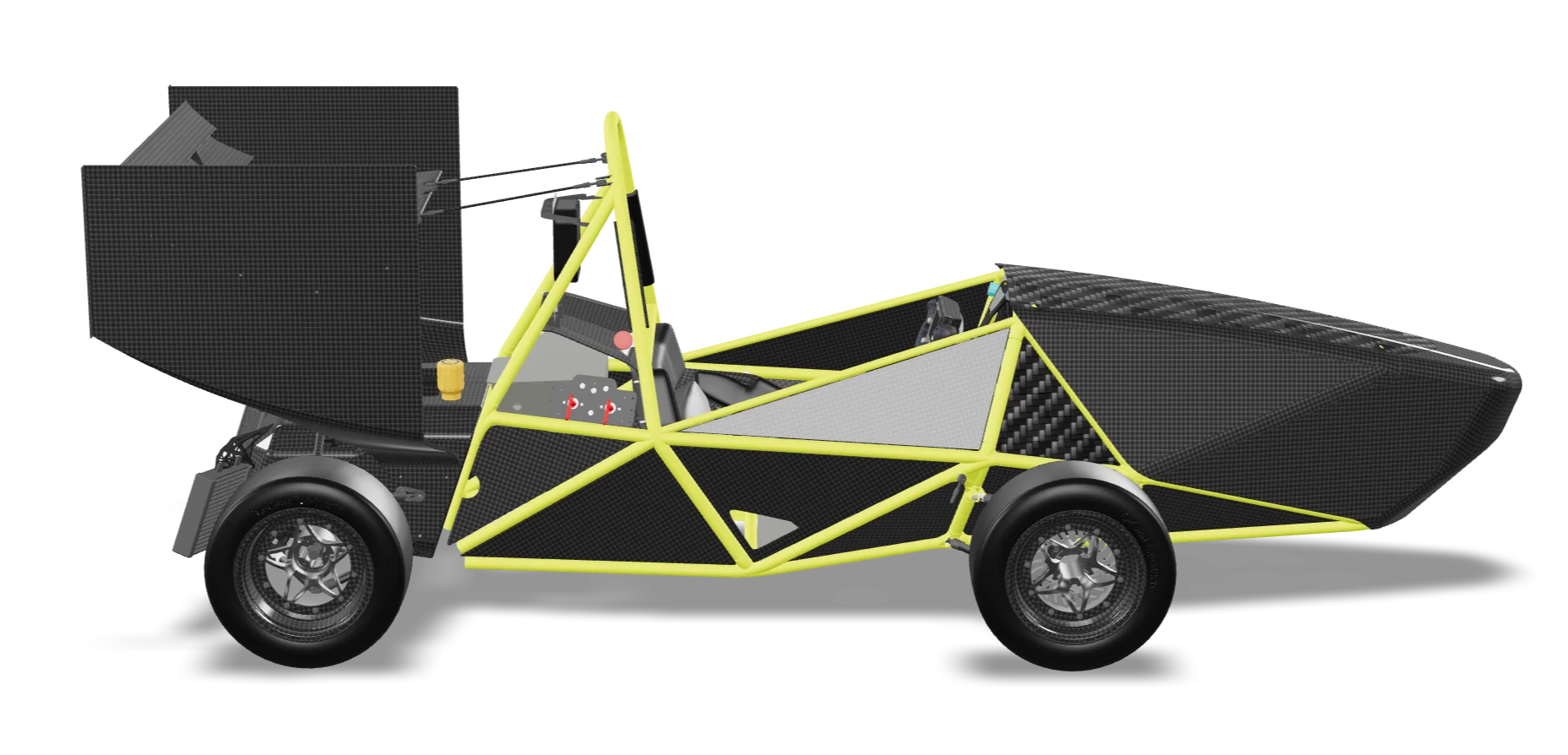
Fenice
Fenice, the second prototype built, was designed during the
pandemic and built despite the problems of lack of
microprocessor availability. It possesses a telemetry solution
inspired by Formula One cars.
At the Riccardo Paletti racetrack in Varano de' Melegari, the
team passed the three static tests, competing against 30 other
international teams in the electric-powered category: the
judges evaluated the prototype by awarding it third place for
the engineering design test, 15th place for the business
presentation test and 19th place for the cost & manufacturing report test.
The team also participated in a number of dynamic tests, obtaining
tenth place in the autocross (timed course of about 800 m to
be completed as quickly as possible) and completing the
endurance (22-km test aimed at evaluating the reliability of
the vehicle) in sixth place.
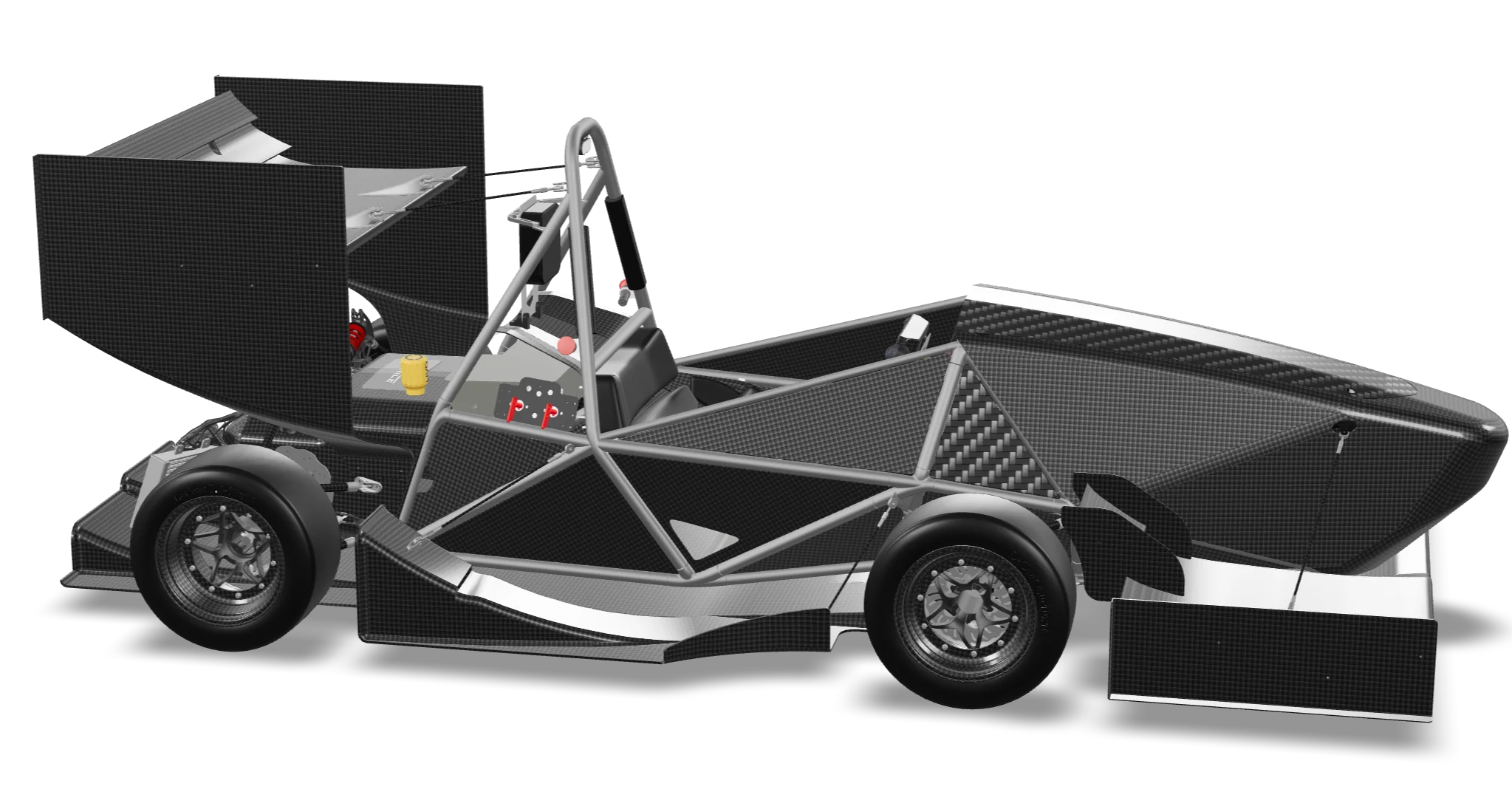


Rear transmission
Dual engine with electronic differential and dynamic
traction control (Torque Vectoring System)
6.5 kWh, air-cooled

Dimensions
Length: 2.70m
Width: 1.50m
Wheelbase:
1.54m
Weight: 210kg

Velocity
Maximum: 130km/h
0-100km/h: <3s
Wheels
LeCont 6x16.00 - 10” (soft compound)
Technical specifications
Velocity
Maximum velocity: 120 km/h
0-100km/h: <3s
Rear transmission
Dual engine with electronic differential and dynamic traction
control (Torque Vectoring System)
Battery
Maximum power: 80 kW (imposed by the regulation)
Power
source: 504V
Capacity: 6.5kWh
Weight: 43kg
Air-cooled
Dimensions
Width: 1.50m
Wheelbase: 1.54m
Weight: 200kg
Weight:
43kg
Wheels
Hoosier 7.5x16.0-10 LC0 (dietro) e 6x16.0-10 LC0 (davanti)
Our results with Fenice

Formula Student Germany
Hockenheimring
Engineering Design: P33
Efficiency: P11
Endurance:
P11
Autocross: P27
Business Plan: P16
Cost & Manufacturing
Report: P49
Overall: P34

Formula ATA
Varano De’ Melegari
Engineering Design: P3
Efficiency: P6
Endurance:
P6
Autocross: P5
Business Plan: P15
Cost & Manufacturing
Report: P19
Overall: P11
Fenice's steering wheel